NTRIP/CORS: How it works and what is involved?
NTRIP, CORS and VRS are different things. However, the terms are often used synonymously in our industry.
NTRIP (Network Transport of RTCM via Internet Protocol) and CORS (Continuously Operating Reference Station) are forms of RTK differential correction that are done through the use of a cellular modem and base station network. This means that instead of using the traditional base station and radio to send correction data to a rover, data is sent using the internet to a cellular modem with a data plan. VRS (Virtual Reference Station) is simply a method of RTK correction that will be explained further later.
In order to use this type of correction you must have a cellular modem, a receiver capable of RTK correction and a cellular data plan. You are also required to register with your local NTRIP provider. This will include creating a username and password as well as obtaining a port and IP address for the cell modem to access the network. Some networks are operated by the state, free of charge, while others are privately operated and can require a subscription fee.
One of the benefits to using NTRIP in areas where available is you are capable of achieving sub-inch RTK accuracies without having to purchase and manage a base station yourself. RTK accuracy allows for a level of repeatability that cannot be achieved through most other types of correction. There are many states that have networks.
The map below shows Minnesota’s network. The base stations are spread generally even to allow for coverage in most areas.
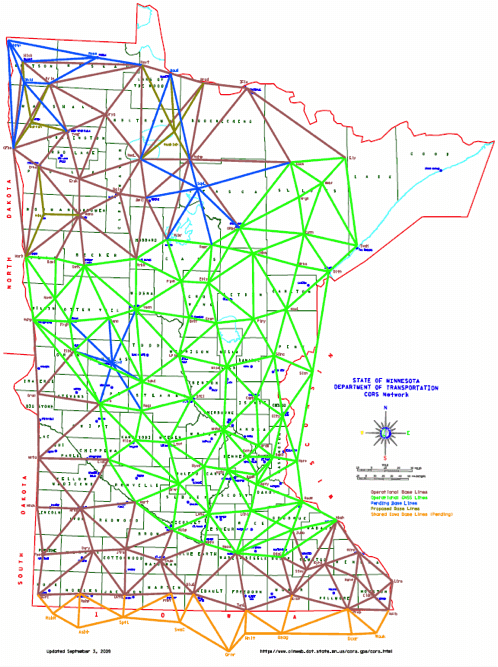
There are four formats supported by NTRIP/CORS: CMR, CMR+, RTCM 2.x and RTCM 3.x. There are five supported NTRIP streams: Near, Max, iMax, Single and VRS.
CMR, CMR+ and RTCM 2.x are only capable of using GPS, whereas RTCM 3.x is capable of using GPS and GLONASS.
Near uses the closest base station in network for its solution, this is based on a GPS position sent from the rover to the network, which chooses the closest base station to the rover. Max and iMax use a network of base stations to create a solution. Max uses a solution generated by the rover whereas iMax uses a solution generated by the server. When using Max all data is sent to the rover and the correction is generated at that location.
When using iMax the receiver periodically sends out its location to the network where the solution is generated and sent back to the rover. Single base is a solution allowed on some networks that lets you choose a specific base station as opposed to having the network choose a base or network of base stations for you. 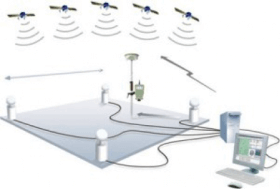 VRS or Virtual Reference Solution requires the rover to send a latitude and longitude position to the VRS network; the network then creates a virtual base close to the rover that is used for correction. The photo below shows an example of a Max solution. There is a network of reference stations that receive information from the GPS network, they communicate through a server and finally a single base sends position information to the rover where the information is corrected.
VRS or Virtual Reference Solution requires the rover to send a latitude and longitude position to the VRS network; the network then creates a virtual base close to the rover that is used for correction. The photo below shows an example of a Max solution. There is a network of reference stations that receive information from the GPS network, they communicate through a server and finally a single base sends position information to the rover where the information is corrected.
Ag Leader offers the ParaDyme® receiver for those interested in using NTRIP/CORS. It includes a built in cell modem. In order to use NTRIP/CORS your ParaDyme must be unlocked for RTK and you must purchase an RTK ReadyConnect Feature Code. ReadyConnect feature codes come in 2 day, 4 month and 10 month increments. The ParaDyme is capable of using CMR+, RTCM 2.x and RTCM 3.x. A GLONASS unlock must be purchased to utilize the additional GLONASS satellites in the RTCM 3.x data stream.